100ms SDK iOS Quickstart Guide
Prerequisites
Familiarity with Xcode and iOS SDK, Cocoapods installed
Xcode Project Setup
Create an Xcode project and select "iOS" for platform and "App" for application
Select "Storyboard" for interface and "Swift" for language
Create "Podfile" in the project folder with the following contents
then run pod install
platform :ios, '13.0' target 'basicvideocall' do use_frameworks! pod 'HMSSDK' end
Open .xcworkspace
Add the entitlements for video, audio and network access to your Info.plist
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key> <string>Please allow access to Camera to enable video conferencing.</string> <key>NSLocalNetworkUsageDescription</key> <string>Please allow access to network usage to enable video conferencing.</string> <key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key> <string>Please allow access to Microphone to enable video conferencing.</string>
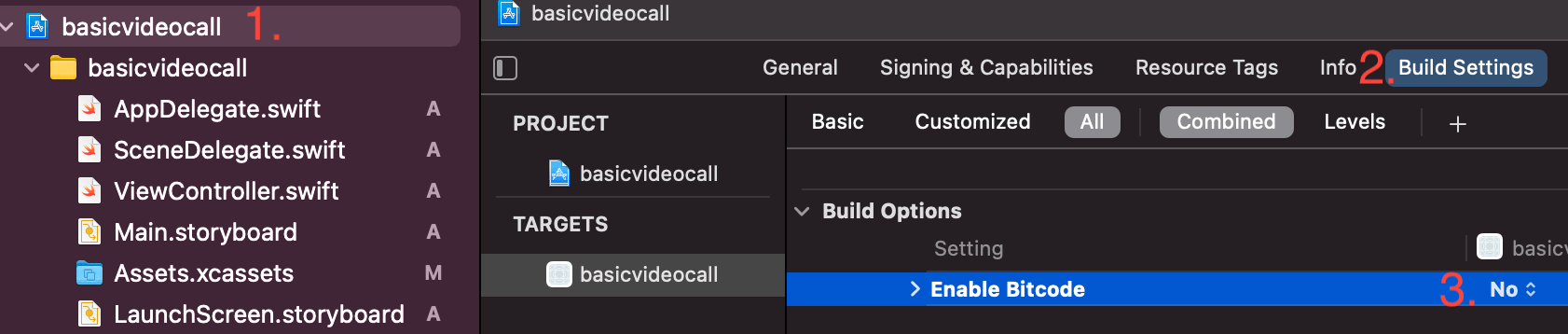
Currently the SDK does not support bitcode so we need to disable it in build settings.
Initialising The SDK
Open ViewController.swift
Add HMSSDK import
import HMSSDK
Conform to HMSUpdateListener and add stubs when Xcode offers to
extension ViewController: HMSUpdateListener { }
class ViewController: UIViewController { var hmsSDK = HMSSDK.build() ... }
Get Auth Token
Before we proceed we need to obtain a room id and a token. In case you are not sure how to do this here is a quick guide:
Join Room
Alright with the token and room id we are ready to proceed.
Add joinRoom() function with room id and token you obtained in previous steps. Then call joinRoom() from viewDidLoad()
func joinRoom() { let config = HMSConfig(userID: UUID().uuidString, roomID: "replace with room id", authToken: "replace with token") hmsSDK.join(config: config, delegate: self) } override func viewDidLoad() { super.viewDidLoad() joinRoom() }
Congratulations! You have an audio conference app.
Build and launch on device, then join same room on web app to try a call between web and iOS.
Adding Video
Lets create add a lazily initialized UIStackView that will hold our video views
class ViewController: UIViewController { var hmsSDK = HMSSDK.build()lazy var stackView: UIStackView = {let result = UIStackView()result.axis = .verticalview.addSubview(result)result.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = falseresult.leadingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.leadingAnchor).isActive = trueresult.trailingAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.trailingAnchor).isActive = trueresult.topAnchor.constraint(equalTo: view.topAnchor).isActive = truelet heightConstraint = result.heightAnchor.constraint(equalToConstant: 0)heightConstraint.isActive = trueheightConstraint.priority = .defaultLowreturn result}()
Next step is to listen for trackAdded update so that we get notified when someone has published a video track.
In the handler we will create an instance of HMSVideoView that allows us to render the HMSVideoTrack
extension ViewController: HMSUpdateListener { ... func on(track: HMSTrack, update: HMSTrackUpdate, for peer: HMSPeer) { switch update { case .trackAdded: if let videoTrack = track as? HMSVideoTrack { addVideoView(for: videoTrack) } default: break } } func addVideoView(for track: HMSVideoTrack) { let videoView = HMSVideoView() videoView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false videoView.setVideoTrack(track) videoView.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: videoView.widthAnchor, multiplier: 9.0/16.0).isActive = true stackView.addArrangedSubview(videoView) }
Build and run the app. Congratulations you have an a/v call running!
Cleanup
A peer can decide to stop publishing any of his tracks at any time (most frequent case is start/stop screen share), also peer may choose to leave a room. In any of these events we want to remove the corresponding video view to release resources.
To start we will introduce a map of track to video view so that we can figure out which video view to remove
class ViewController: UIViewController { var hmsSDK = HMSSDK.build()var trackViewMap = [HMSTrack: HMSVideoView]()...
Next we want to add a map entry as a last step in our addVideoView function
func addVideoView(for track: HMSVideoTrack) { let videoView = HMSVideoView() videoView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false videoView.setVideoTrack(track) videoView.heightAnchor.constraint(equalTo: videoView.widthAnchor, multiplier: 9.0/16.0).isActive = true stackView.addArrangedSubview(videoView) trackViewMap[track] = videoView }
Now we will create a helper function that will remove the view for given track
func removeVideoView(for track: HMSVideoTrack) { trackViewMap[track]?.removeFromSuperview() }
With this we are ready to add handlers for trackRemoved and peerLeft events as follows:
func on(peer: HMSPeer, update: HMSPeerUpdate) { switch update { case .peerLeft: if let videoTrack = peer.videoTrack { removeVideoView(for: videoTrack) } default: break } } func on(track: HMSTrack, update: HMSTrackUpdate, for peer: HMSPeer) { switch update { case .trackAdded: if let videoTrack = track as? HMSVideoTrack { addVideoView(for: videoTrack) } case .trackRemoved: if let videoTrack = track as? HMSVideoTrack { removeVideoView(for: videoTrack) } default: break } }
And that's how you handle most common use case with the 100ms SDK!
Final Points
To control mute/unmute state of local video and audio tracks use
hmsSDK.localPeer?.localAudioTrack()?.setMute(true) hmsSDK.localPeer?.localVideoTrack()?.setMute(true)
After you are done with the call it is a good idea to call
hmsSDK.leave()
Ways to go from here
Checkout complete project code on github: https://github.com/100mslive/100ms-ios-sdk/tree/main/BasicExample
Checkout a sample code for a full featured conferencing app:
https://github.com/100mslive/100ms-ios-sdk/tree/main/Example